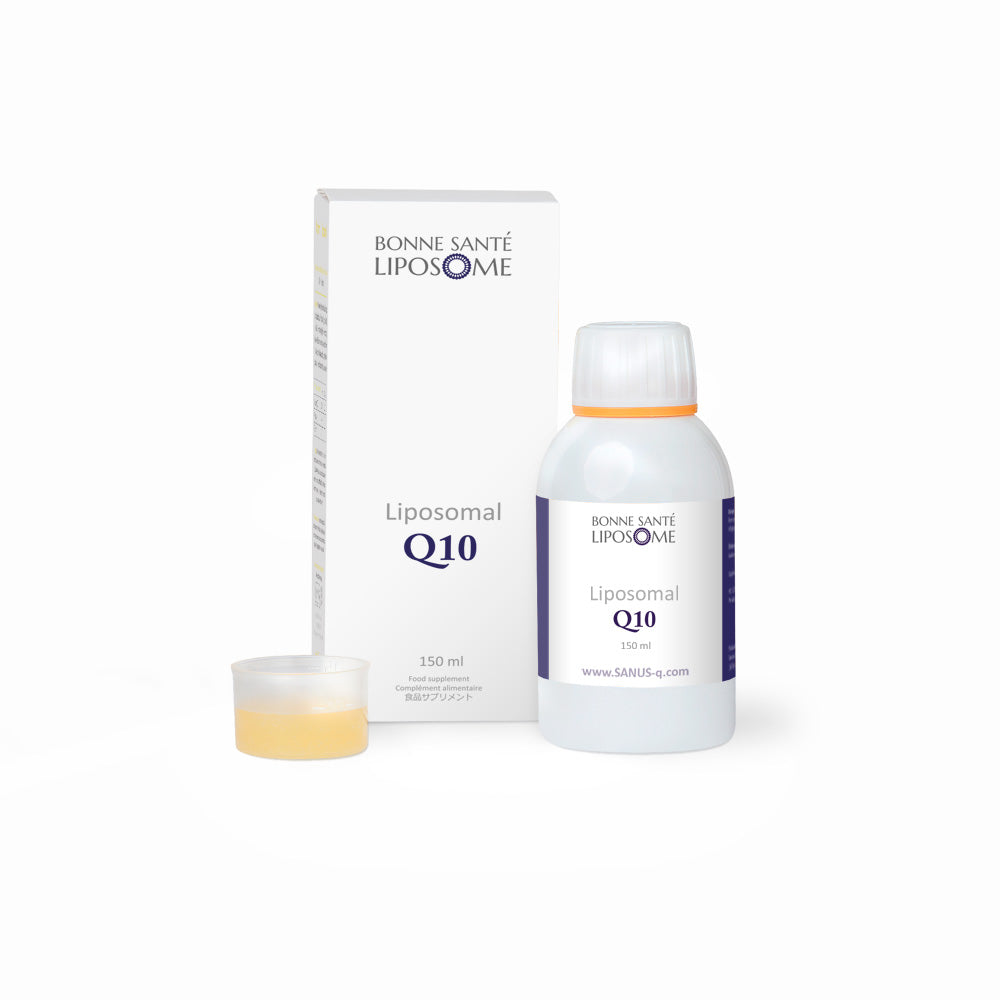
Bonne Santé Liposome: Liposomal CoQ10 (CoQ-10 as ubiquinone) - 150ml
Liposomal CoQ10 for healthy heart, improved energy and anti-aging benefits
Current batch best before date: Product discontinued
(Check our current promotions before buying)
Contains: (per 5 ml) 200 mg Co-enzyme Q10 (ubiquinone)
Suggested dosage: 1 x 5 ml directly in mouth or glass of water or juice, unless otherwise advised by a healthcare professional. Do not exceed recommended dosage.
Ingredients: Co-enzyme Q10; lecithin (Non-GMO SOY) - emulsifier; glycerol - humectant; ethanol <4.2%; natural vitamin E (as d-alpha tocopherol) - antioxidant; potassium sorbate - preservative; purified water.
Recommended serving size: 5 ml
Servings per bottle: 30
Storage: Store cool and dry. When opened store in refrigerator and finish within 2 months.
Product description PDF: View Here
Product Description
- 150 ml CoQ10
- Use of liposomal technology for better absorption and bio-availability
- Non-GMO product
- Measuring cup included
- Resealable screw top lid
CoQ10 Health Benefits
- Improves energy levels
- Supports heart function and health
- Effective in migraines
- Fights gum disease
- Reduces side effects associated with statins
- Prevents premature aging
Why do you need CoQ10?
CoQ10, also known as ubiquinone and as ubiquinol, is a coenzyme produced naturally by the body. Ubiquinone (oxidized form) is essential for CoQ10’s role in cellular energy metabolism (ATP synthesis) and ubiquinol (reduced form) is essential for the antioxidant function of CoQ10.
Fish (sardine and mackerel), beef and organ meats such as heart, liver and kidney are the richest source of CoQ10 in diet. Other foods that are also a good source include spinach, cauliflower, broccoli, lentils, peanuts, and soy oil.
CoQ10 levels typically decline with age. Statins also deplete CoQ10 levels in your body. Many other factors - such as low levels of B vitamins, chronic infections, stress, smoking and long-term use of certain medications including beta-blockers, antidepressants, anti-diabetes medications, diuretics and antibiotics – also cause CoQ10 deficiency. Low levels of CoQ10 have been linked to many health conditions, such as heart failure, diabetes, high blood pressure, gum disease, infertility, fibromyalgia and cancer.
CoQ10 offers tremendous benefits to your health. This is due to two very important roles that it plays in the body: in producing energy and as a power antioxidant.
Ubiquinone versus ubiquinol
There has been some debate for the past several years in regard to what form of CoQ10 is best: ubiquinone or ubiquinol.
The fact is you need both forms of CoQ10:
Ubiquinone, the oxidized form is required for the production of energy (ATP). This is due to its ability to accept electrons in chemical reactions that lead to ATP synthesis. Ubiquinol, the reduced form is responsible for its anti-oxidant properties. This is due to its ability to donate electrons to free radicals.
Your body knows how to maintain the balance between these two forms. It senses what it needs and is very much capable of transforming one form into another accordingly. In a nutshell, it doesn’t really matter which form of CoQ10 you take. When the oxidized form of CoQ10 (ubiquinone) is used by the body to create energy, it is converted into its reduced form (ubiquinol). In the same way, when ubiquinol is used up to neutralize free radicals and toxins in the body, it becomes ubiquinone.
In addition, most studies (like the famous Q-Symbio clinical trial, that highlights the benefits of CoQ10 in patients with heart failure) have used CoQ10 in ubiquinone form.
Since the two different forms of CoQ10 can easily be converted from one form to the other, we feel that it makes sense to stick with a form that is more affordable and to pass those savings to our valued customers. Ubiquinone is less expensive to process and manufacture. It is also important to note that ubiquinol is unstable in standard capsule form.
Crucial role in energy production
The mitochondria, powerhouse of cells, convert the food into energy through a complex series of chemical reactions. CoQ10 plays a unique, ‘one of a kind’ role in these reactions. Low CoQ10 levels means less energy for cellular functions and poor mitochondrial health.
Role as an antioxidant
CoQ10 is a powerful antioxidant that fights and destroys excess free radicals, molecules that cause oxidative damage to the cells and their components like DNA, proteins, lipids and mitochondria, by stealing their electrons. Free radicals cause oxidative damage and inflammation – associated with premature aging at cellular levels. CoQ10 is also responsible for regenerating other antioxidants like vitamins C and E. This further improves the body’s ability to counter oxidative damage.
The majority of the health problems that we face today are rooted in oxidative stress, inflammation and mitochondrial dysfunction (which impairs energy production in the cells). That is why CoQ10 – with its important role in reducing oxidative damage, generating cellular energy and improving mitochondrial functions – may have protective effects in various conditions.
1. CoQ10 in heart health
CoQ10 is one of the best supplements for you heart. It helps your heart keep pace with high energy demands and also offers other benefits:
- Improves symptoms in people with congestive heart failure; and also lowers the risk of unexpected hospitalization or urgent transplantation. [1]
- Improves endothelial functions
- Prevents oxidation of LDL cholesterol, reducing the risk of atherosclerosis
- Improves symptoms of angina and increases exercise capacity in people with angina
- Improves endothelial functions and lowers blood pressure
- Reduces the adverse effects of statins on heart health
2. CoQ10 in statin use
Statins are the drugs routinely prescribed to lower cholesterol levels. These drugs work by blocking the enzyme pathway that produces cholesterol. Since this pathway also makes CoQ10 (along with other important molecules such as vitamin k2, bile and heme), prolonged use of statins decreases CoQ10 levels in the body.
Low levels adversely affect your muscular organ health (ie. Heart) and brain – causing side effects like fatigue, muscle pain, muscle weakness and brain fog. Co10 supplements can reduce muscular organ (and brain) related symptoms caused by statins. [2]
3. CoQ10 in anti-aging
CoQ10 prevents premature aging in the body and reduces the risk of associated diseases: [3]
- Improves mitochondrial function
- Improves availability of energy in tissues,
- Lowers oxidative stress in cells and mitochondria,
- Reduces inflammation, associated with age-related degenerative health conditions
CoQ10 supplement is useful in many other conditions, where mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative damage play a significant role
- Male and female infertility: In men, it improves the quality and quantity of sperm count. In woman, it reverses age-related decline in egg number and quality.
- Gum disease: Reduces inflammation in the gum and improves symptoms of swelling, redness and pain. In addition, CoQ10 deficiency increases your risk of getting periodontal (gum) disease.
- Migraines: Lowers the frequency and severity of migraines. [4]
- Fibromyalgia: shown to improve symptoms like pain, headache, fatigue and morning tiredness. [5]
- Type 2 diabetes: Reduces blood glucose levels. CoQ10 supplements also show protective effects on diabetic retinopathy, a common microvascular complication associated with diabetes. It is caused when high blood sugar levels damage the blood vessels in the retina, leading to blurred vision and even vision loss if not treated in a timely manner. [6] [7]
Bonne Sante Liposome Co-enzyme Q10
Our CoQ10 supplement uses liposomal technology for enhanced absorption and bioavailability. This means your body will be able to use and absorb CoQ10 more efficiently. Most supplements, when taken orally, are wasted in the digestive tract and only a small amount is available for the cells. On the other hand, in liposomal form, the nutrients are delivered directly to the bloodstream and cells.
Always consult your doctor before taking any supplement. This product is not recommended during pregnancy and breastfeeding. It is also not meant for small children. CoQ10 supplements may interfere with any pre-existing health conditions, drugs or herbal supplements you are taking.
References:
- A Sharma et al. Coenzyme Q10 and Heart Failure. A State-of-the-Art Review. Circulation. Heart Failure. 2016.
- Skarlovnik et al. Coenzyme Q10 Supplementation Decreases Statin-Related Mild-to-Moderate Muscle Symptoms: A Randomized Clinical Study. Medical Science Monitor. 2014
- JD Hernández-Camacho et al. Coenzyme Q10 Supplementation in Aging and Disease. Front Physiol. 2018
- Shoeibi et al. Effectiveness of coenzyme Q10 in prophylactic treatment of migraine headache: an open-label, add-on, controlled trial. Acta Neurol Belg. 2017
- Cordero et al. Oxidative stress correlates with headache symptoms in fibromyalgia: coenzyme Q₁₀ effect on clinical improvement. 2012 PLoS One.
- D. Mantle. Coenzyme Q10 supplementation for diabetes and its complications: an overview. Br J Diabetes. 2017.
- Ates et al. Plasma coenzymeQ10 levels in type2 diabetic patients with retinopathy. Int J Ophthalmol. 2013.


 Pin it
Pin it