Health on Your Terms
What are liposomes?
- Home
- What are liposomes?
So, what exactly is a liposome? And how does it work?
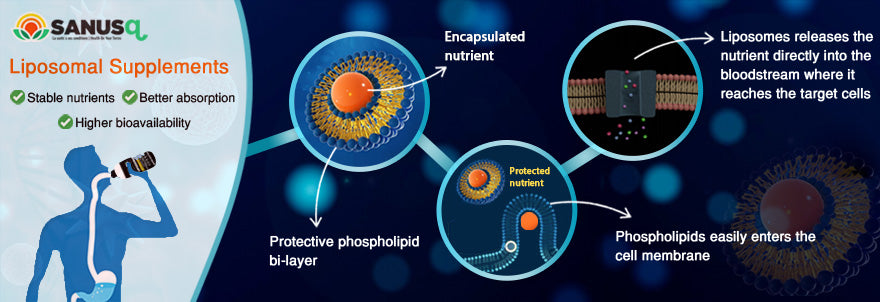
When you ingest traditional supplements orally, their content undergo decomposition at many levels in the digestive system, thus resulting in low bioavailability and a low absorption rate. With liposomal technology, nutrient payloads bypass these degradation steps, and the active ingredient or enclosed nutrient is directly released into the bloodstream and from there into the cells and tissues, where it needs to be.
Liposomes have emerged as very efficient drug carrier systems that make nutrients and other therapeutic agents more bio-available within the body. You may have heard of liposomal supplements but do you know why are they so fantastic?
The word ‘liposome’ is derived from two Greek words: 'Lipos' (which means fat) and 'Soma' (which means body). Liposomes were first discovered in 1964 by Alec Bangham and his colleague R.W. Thorne when they were examining a dispersion of phospholipids in water under an electron microscope. Today, liposomes are used as structures that encapsulate and carry drugs, nutrients and cosmetic agents directly to the cells and tissues for improved uptake and absorption.
A liposome is a very small spherical vesicle made up of phospholipids – a type of lipid that is a major structural component of our cell membranes (the outer layer of the cells).
More about phospholipids
One of the most important functions of the phospholipids is to regulate the transport of nutrients and other substances across the cell membrane. In this capacity, these molecules work as ‘gatekeepers’ and play an integral role in determining what goes in and out of the cell.
Other functions of phospholipids are:
- Allow cell membranes to be fluid, which helps cells to change shape to adapt to environmental challenges
- Work as signalling molecules or messengers in cellular communication systems (for example, phospholipid molecules signal white blood cells to travel to a site of infection or injury)
- Protect cell membranes against oxidative damage caused by free radicals
How do liposomes work as ideal drug delivery systems?
First, it is important to understand the structure of phospholipids, as it holds the key to how liposomes work.
- A phospholipid molecule consists of 2 fatty acid chains (tail) and a phosphate group (head). These two components are joined together by a glycerol molecule.
- The fatty acid chains or tails are ‘hydrophobic’ (repelled by water).
- The phosphate end or head is ‘hydrophilic’ (attracted by water).
In an aqueous solution, the phospholipids molecules automatically self-assemble in such a way that the hydrophobic fatty acid tails move away from the water and turn inward; whereas the water loving phosphate head moves toward the liquid and turns outward. This self-arrangement results in a closed, spherical structure, called liposomes, with a hollow aqueous core surrounded by a double-layer (bi-layer) membrane.
In liposomal supplements, the active ingredients (such as nutrients or medicines) are loaded into these microscopic vesicles, to be carried and delivered to the cells. The interesting thing is that these vesicles can encapsulate both water soluble substances in the central aqueous space as well as fat soluble nutrients within the membranes.
Benefits of using liposomal encapsulated technology
Liposomes form a protective barrier around their ‘encapsulated contents’. This barrier protects the nutrients/drugs against degradation by enzymes present in the mouth and stomach, digestive juices, bile acids and intestinal micro-organisms. Liposomes also shield the nutrients against free radicals.
“This protective phospholipid shield or barrier remains undamaged until the contents of the liposome are delivered to the exact target gland, organ, or system where the contents will be utilized.” [1]
When you ingest traditional supplements orally, their content undergo decomposition at many levels in the digestive system, thus resulting in low bio-availability and a low absorption rate. With liposomal technology, nutrient payloads are able to bypass these degradation steps and the enclosed nutrient is directly released into the bloodstream and from there into the cells and tissues, where it needs to be.
What also works in favour of liposomes is that they are composed of the same fat that your membranes are made up of. This allows liposomes to easily penetrate the cell membrane barrier and reach the target cell. In a nutshell, liposomal supplements offer the following benefits:
- Improved bio-availability of nutrients
- Enhanced uptake and absorption of nutrients by cells and tissues
- No gastrointestinal distress often experienced when a high dose of supplements is taken orally.
Liposomal encapsulation of therapeutic agents is a ground-breaking delivery process, a fact that is supported by decades of studies.
- “Use of liposomes as delivery vehicles for sustained (vitamin) release and controlled absorption could be a promising approach for improving the therapeutic potency of active pharmaceutical ingredients.” [2]
- “Because of their unique properties liposomes are able to enhance the performance of products by increasing ingredient solubility, improving ingredient bioavailability and in vitro and in vivo stability.” [3]

Research has also supported the use of liposomes to administer anti-tumor drugs to improve their efficacy and reduce the toxic side effects. [4] [5]
References:
- Hemanthkumar M, Spandana V. Liposomal encapsulation technology a novel drug delivery system designed for ayurvedic drug preparation. IRJP. 2011.
- Yang Z et al. Effect of liposomes on the absorption of water-soluble active pharmaceutical ingredients via oral administration. Curr Pharm Des. 2013
- BC Keller. Liposomes in nutrition. Trends in Food Science & Technology
- Melissa A. Tran et al. Use of Liposomes as Drug Delivery Vehicles for Treatment of Melanoma. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2009 Aug; 22(4): 388–399.
- Safra T et al. Pegylated liposomal doxorubicin (Doxil): reduced clinical cardiotoxicity in patients reaching or exceeding cumulative doses of 500 mg/m2. Ann. Oncol. 11 (2000) 1029
